Basic Concepts of Interest Rates
Basic Concepts of Interest Rates
Visit the Mathema Option Pricing System, supporting FX options and structured product pricing and valuation!
The following is a detailed expansion and sorting of relevant concepts in the process of constructing interest rate curves, combined with definitions, formulas, characteristics, and application scenarios, in order to have a more comprehensive understanding of these important concepts commonly found in the interest rate market.
1. Zero-Coupon Rate
Definition
- The zero-coupon rate refers to the yield to maturity implied by a zero-coupon bond. A zero-coupon bond is a bond that does not pay periodic interest but pays the principal and interest in a lump sum at maturity.
- It is an interest rate with no intermediate cash flows, calculated solely based on the return from holding the bond until maturity.
Characteristics
- No Intermediate Payments: Only a single payment of principal and interest at maturity.
- Yield to Maturity: The zero-coupon rate directly reflects the return an investor earns by holding the bond until maturity.
- Foundation for Building the Term Structure: Zero-coupon rates are used to construct interest rate curves (e.g., the zero-coupon rate curve).
Formula
The relationship between the price of a zero-coupon bond and the zero-coupon rate:
Where:
- : Current price of the zero-coupon bond.
- : Face value of the bond.
- : Zero-coupon rate.
- : Time to maturity.
Applications
- Term Structure Construction: Calculating zero-coupon rates for different maturities using zero-coupon bond pricing.
- Present Value Calculation: Used to calculate the present value of future cash flows.
2. Spot Rate
Definition
- The spot rate refers to the risk-free interest rate for different maturities at the current moment. It is a manifestation of the zero-coupon rate, reflecting the market's pricing of funds for different maturities.
Characteristics
- Maturity Dependency: The spot rate varies with maturity, forming the term structure of interest rates.
- Market Benchmark: The spot rate is a crucial basis for pricing bonds, derivatives, and other financial instruments.
Formula
The relationship between the spot rate and the zero-coupon rate:
Here, the spot rate is directly equivalent to the zero-coupon rate .
Applications
- Bond Pricing: Using the spot rate to discount future cash flows.
- Derivative Pricing: Such as option pricing and swap pricing.
3. Forward Rate
Definition
- The forward rate refers to the interest rate starting at a future point in time, derived from the current spot rate. It represents the market's implied expectation of future interest rates.
- Forward rates are not directly observable but are calculated from spot rates.
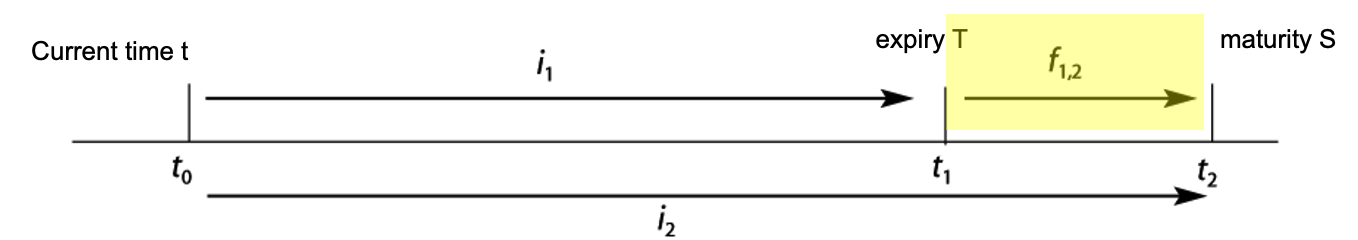
Characteristics
- Implicit Nature: Forward rates reflect the market's expectations of future interest rates.
- Risk Hedging Tool: Used to lock in future borrowing costs or investment returns.
Formula
Under simple interest, the forward rate derived from spot rates:
Where:
- , : Spot rates for maturities and , respectively.
- : Forward rate from to .
Applications
- Bond Investment Strategies: Analyzing forward rates to predict future yield changes.
- Interest Rate Derivatives: Such as pricing forward rate agreements (FRAs) and interest rate swaps.
4. Yield to Maturity (YTM)
Definition
- The yield to maturity is the discount rate that equates the present value of a bond's future cash flows to its current price.
- It is a comprehensive yield measure that considers the coupon rate, market price, and time to maturity.
Characteristics
- Comprehensive: YTM is a comprehensive yield metric that reflects market price and bond characteristics.
- Non-Fixed: YTM fluctuates with changes in market prices.
- Iterative Calculation: YTM is typically calculated using numerical methods.
Formula
The relationship between bond price and yield to maturity :
Where:
- : Periodic coupon payment.
- : Face value.
- : Time to maturity.
Applications
- Bond Pricing: YTM is a key pricing metric for bond investments.
- Yield Comparison: Used to compare the investment value of different bonds.
5. Coupon Rate
Definition
- The coupon rate is the fixed interest rate set at the issuance of a bond, used to calculate the periodic coupon payments.
- The coupon rate is based on the bond's face value.
Formula
Calculation of periodic coupon payment :
Applications
- Interest Payments: Used to calculate the bond's cash flows.
- Bond Pricing: The coupon rate influences the bond's market price.
6. Coupon Rate in Interest Rate Swaps (IRS)
Definition
- In an interest rate swap (IRS), the coupon rate is the fixed rate paid by the fixed-rate payer.
- The coupon rate is typically equal to the par rate, which is the fixed rate that makes the swap's present value zero.
Characteristics
- Market-Driven Pricing: The coupon rate is an agreed-upon rate by market participants.
- Alignment with Par Rate: The swap rate is usually equal to the par rate.
7. Par Rate
Definition
- The par rate is the interest rate that makes the bond's current price equal to its face value.
- It reflects the market's discount rate and is a key reference for bond pricing.
Formula
The present value formula for the par rate:
When , is the par rate.
8. Discount Factor
Definition
- The discount factor is the present value coefficient of a future cash flow at the current moment.
- It directly reflects the time value of money and the level of interest rates.
Formula
Calculation of the discount factor :
Under continuous compounding:
Applications
- Bond Pricing: Used to discount future cash flows.
- Derivative Pricing: Widely applied in pricing models for options, futures, etc.
Summary and Comparison
| Concept | Definition | Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zero-Coupon Rate | Yield to maturity of a zero-coupon bond | No intermediate payments, yield to maturity | Term structure construction, present value calculation |
| Spot Rate | Risk-free interest rate at the current moment | Maturity-dependent | Bond pricing, present value calculation |
| Forward Rate | Implied interest rate starting at a future point | Reflects market expectations of future rates | Interest rate derivatives, bond investment |
| Yield to Maturity | Discount rate equating bond's cash flow present value to its current price | Comprehensive yield, considers coupon, price, and maturity | Bond pricing, yield comparison |
| Coupon Rate | Fixed interest rate set at bond issuance | Fixed rate, used to calculate coupon payments | Bond cash flow calculation |
| Coupon Rate in IRS | Fixed rate paid by the fixed-rate payer in an IRS | Typically equals the par rate | Interest rate swap pricing |
| Par Rate | Interest rate making bond price equal to face value | Market discount rate | Term structure construction |
| Discount Factor | Present value coefficient of future cash flows | Closely related to interest rates | Bond pricing, derivative pricing |
