Structured Products for Exchange Rate Hedging – Zero-Cost Collar
Structured Products for Exchange Rate Hedging – Zero-Cost Collar
Visit the Mathema Option Pricing System for foreign exchange options and structured product valuation!
What is a Zero-Cost Collar?
A Zero-Cost Collar is an options strategy designed to protect traders from potential downside risks. It achieves this by using a combination of call and put options that effectively offset each other.
While this strategy limits potential losses, it also caps potential profits. It effectively hedges against fluctuations in the underlying asset's price.
When to Use a Zero-Cost Collar Strategy
This strategy involves buying a call option and selling a put option. The strike price of the sold put option is set such that the premium received equals the premium paid for the call option.
The collar strategy is used to protect an existing long position at a relatively low cost, as the premium paid for the call option is offset by the premium received from selling the put option.
Pros and Cons Analysis (For Enterprises)
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| For investors with a basic understanding of options and stock trading but who are not yet seasoned professionals, the learning and operational barriers to implementing this strategy are relatively moderate. Its logic is easy to grasp and put into practice. Both risks and returns are controllable, allowing investors to clearly understand the maximum potential losses and gains. This facilitates precise risk-return planning and provides a greater sense of control amid market fluctuations. As a capital gains-oriented strategy, it primarily generates profits through price fluctuations of the underlying asset, aligning with the conventional logic of profiting from asset price movements. This makes it more accessible and easier to adopt. | In environments with significant changes in market volatility, it lacks the flexibility of certain volatility-dependent options strategies (such as straddles or strangles) and cannot capture additional gains from volatility shifts. Limited profit growth, Due to the cap on maximum returns, investors cannot fully capitalize on unexpectedly large price surges in the underlying asset, restricting the potential for higher profits. Complex asset portfolio,Compared to stock or options trading, this strategy involves more operational steps, requiring simultaneous management of multiple positions. This places higher demands on trade execution and position monitoring. |
Example of a Zero-Cost Collar Strategy
The payoff of a Zero-Cost Collar is shown below:
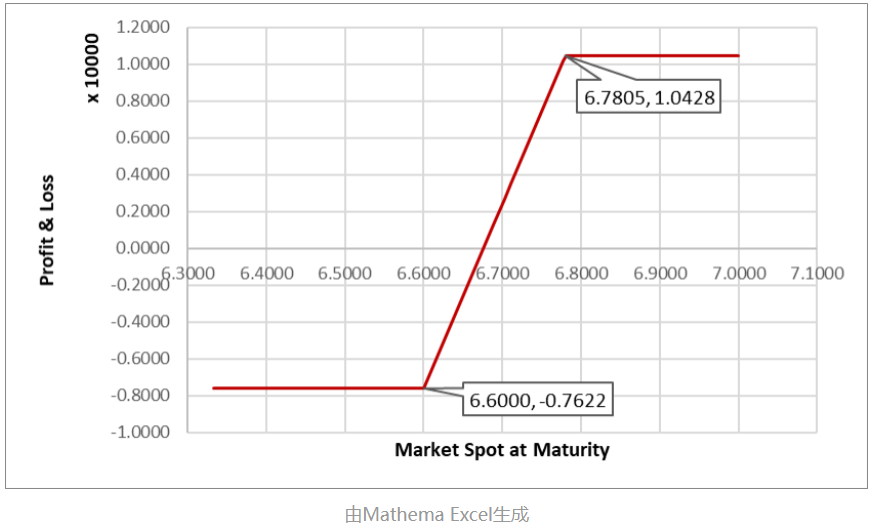
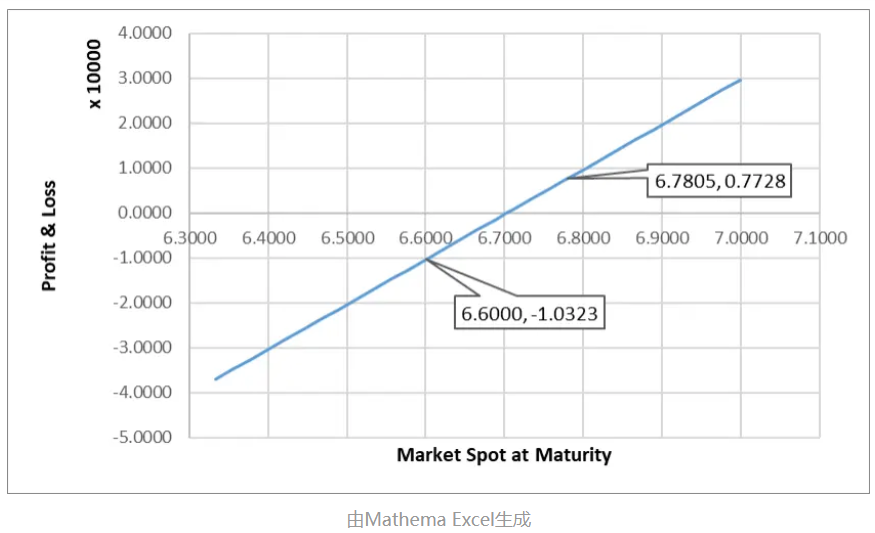
For example, an exporter expects to receive $100,000 in one year. The current spot exchange rate is 6.55, and the one-year forward rate is 6.7032. Without any hedging, if the exporter does not hedge at all, the profit and loss relative to the current forward rate when settling at the spot rate in one year would be:
If the exchange rate falls (CNY appreciates), the company faces exchange rate risks. If the company seeks to protect its foreign exchange exposure while also expecting the CNY to depreciate further in the coming year, the company's options trader can sell a one-year call option on $100,000 with a strike price of 6.7805 for $1,532 and use the proceeds to buy a one-year put option on $100,000 with a strike price of 6.600, creating a Zero-Cost Collar.
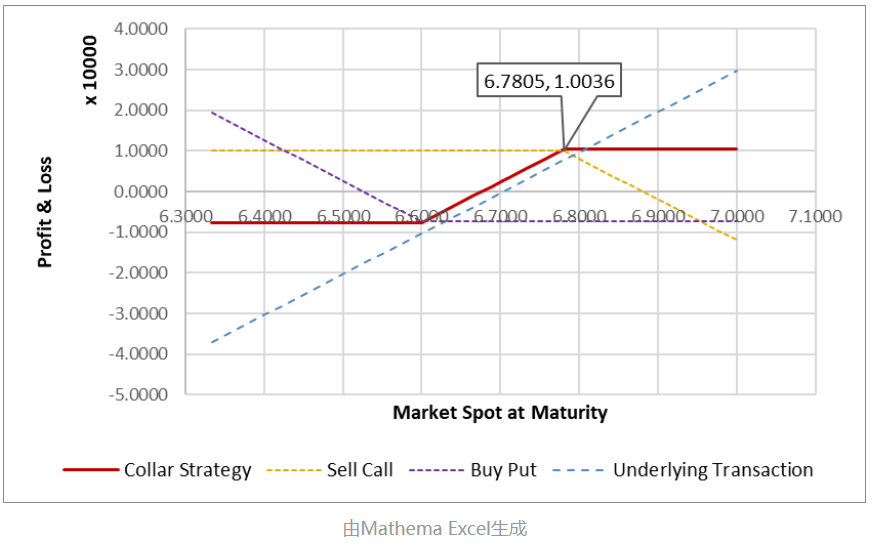
As shown in the figure above, if the exchange rate falls below 6.600, the company's loss is fixed. Similarly, if the exchange rate rises above 6.7805, the maximum profit is also capped (profit: CNY 10,003.6).
Disadvantages of the Zero-Cost Collar Strategy
The pros and cons of the collar strategy are obvious. The transaction itself incurs no additional premium, and the maximum future loss is fixed. However, it does involve the opportunity cost of giving up potential gains, as profits are also capped. For those with experience in options trading, the collar strategy may prove to be productive.
Difference Between Collar and Range Forward
When researching collars and range forwards, it was found that definitions of Collar and Range Forward vary across sources. Here, we define Range Forward as follows:
A Range Forward (also known as Spread Forward or Risk Reversal) typically involves buying a call option and selling a put option, or selling a call option and buying a put option. The premiums of these options are generally equal, offsetting each other to form a zero-cost or low-cost options combination, which is one of the most distinctive features of the range forward strategy.
The profit and loss/expiration spot price chart for a range forward is as follows:
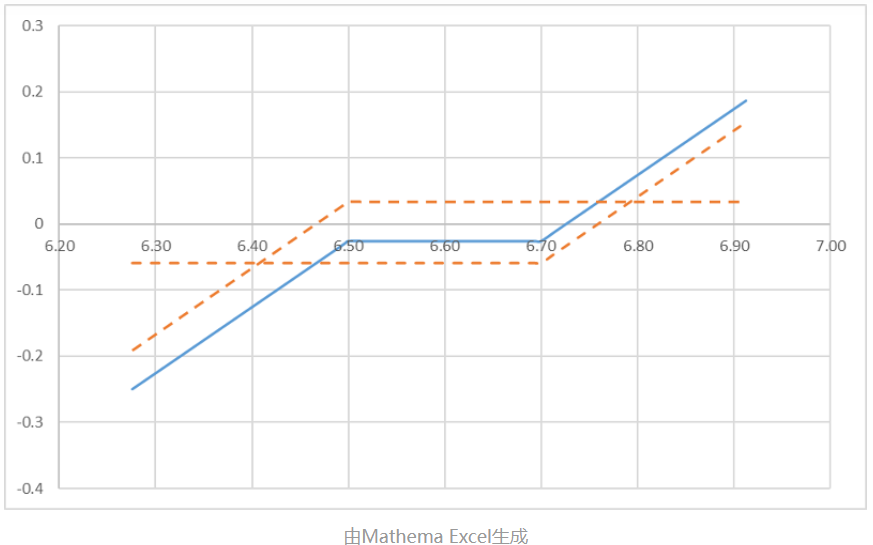
For a detailed description, please refer to: Structured Products for Exchange Rate Hedging – Range Forward.
