Structured Products for Exchange Rate Hedging – Seagull Forward
Structured Products for Exchange Rate Hedging – Seagull Forward
Visit the Mathema Option Pricing System for foreign exchange options and structured product valuation!
Business Overview
The Seagull Forward, also known as the Seagull Option, Rambo Option Combination, or Stair Case Strategy, can be decomposed into three standard options: one long option and two short options, resulting in four possible settlement outcomes.
Product Features
The Seagull Option combination allows traders to engage in the market with minimal premium outlay. For companies selling foreign exchange, a bullish outlook can be implemented by buying a higher-strike put option and selling a lower-strike put option to reduce premium costs, while also selling a higher-strike call option to further lower the average cost. However, if the price exceeds the highest strike call option, the company may face unlimited risk.
Pros and Cons Analysis (For Enterprises)
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Limited upside potential with a forward price better than the forward exchange rate. | If the price exceeds the highest strike call option, the company may face unlimited risk. |
| Compensation if the domestic currency depreciates, but no protection beyond a certain level. | Protection only applies if the exchange rate falls below a specified level at maturity. |
| No fees or separate charges. | |
| Customizable exchange rate levels based on expectations, plans, and budgets. | |
| Can be closed early through a reverse transaction if hedging is no longer needed. | Early closure may result in profits or losses depending on market conditions. |
Case Study
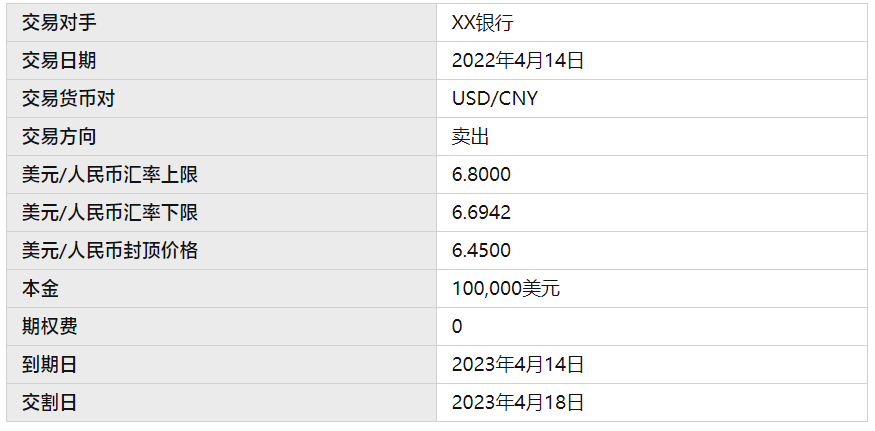
On March 3, 2018, the spot price was 6.55, and the direct forward price was 6.7301. A company plans to settle $100,000 in foreign exchange in one year.
The bank's operation involves creating a foreign exchange put risk reversal option combination with a range of [6.6942, 6.8000]. This includes:
- Buying a lower-strike put option (6.45).
- Selling a higher-strike call option (6.8000).
- Selling an even lower-strike put option (6.45).
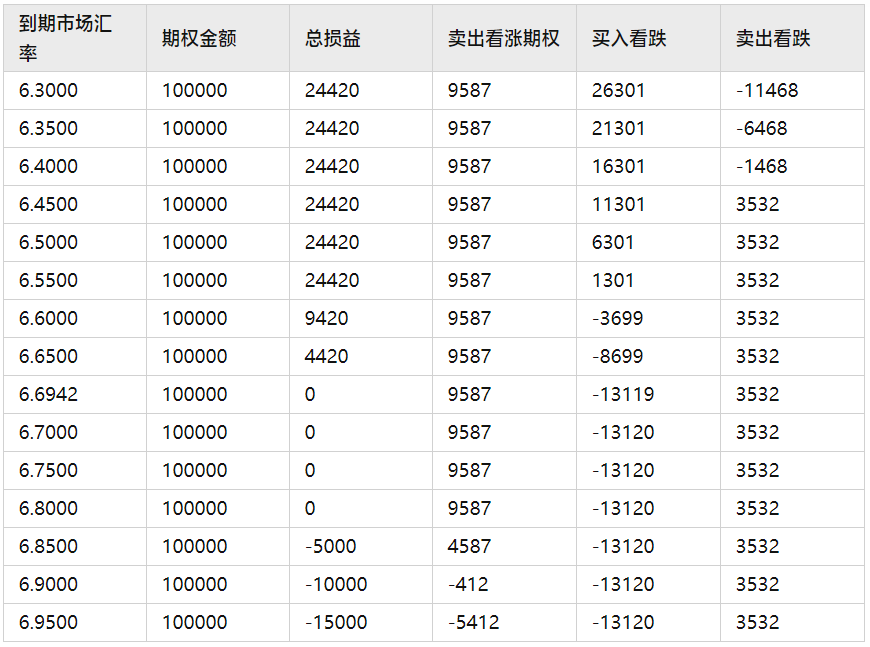
At settlement, there are four scenarios:
A. If the market rate is below 6.45: Both the bought and sold put options are exercised, locking the settlement price at 0.2442 (=6.6942 - 6.4500).
B. If the market rate is between [6.54, 6.6942]: Only the bought put option with a strike of 6.6942 is exercised, resulting in a settlement price of 6.6942 (slightly better than the market forward price of 6.7031).
C. If the market rate is between [6.6942, 6.8]: None of the options are exercised.
D. If the market rate is above 6.8: Only the sold call option with a strike of 6.8 is exercised, exposing the company to risk.
The components of the combined option are as follows:
Pricing Analysis
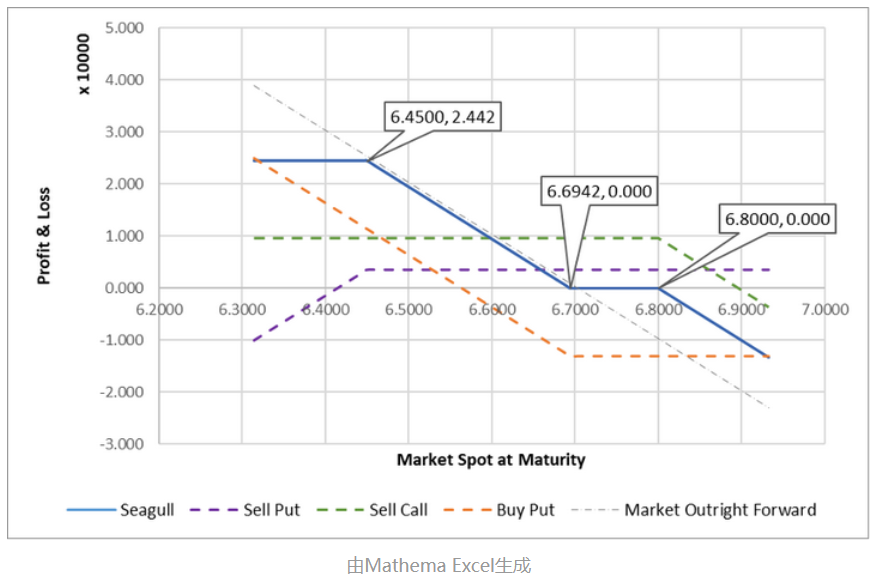
As shown in the case study, for a company selling foreign exchange, a Seagull Forward (selling USD/buying CNY) can be decomposed into three options:
- Buy USD Put @ Lower Strike Price
- Sell USD Call @ Upper Strike Price
- Sell USD Put @ Cap Price (Note: Cap Price < Lower Strike Price < Upper Strike Price)
The profit and loss analysis of the Seagull Forward as the exchange rate fluctuates is as follows:
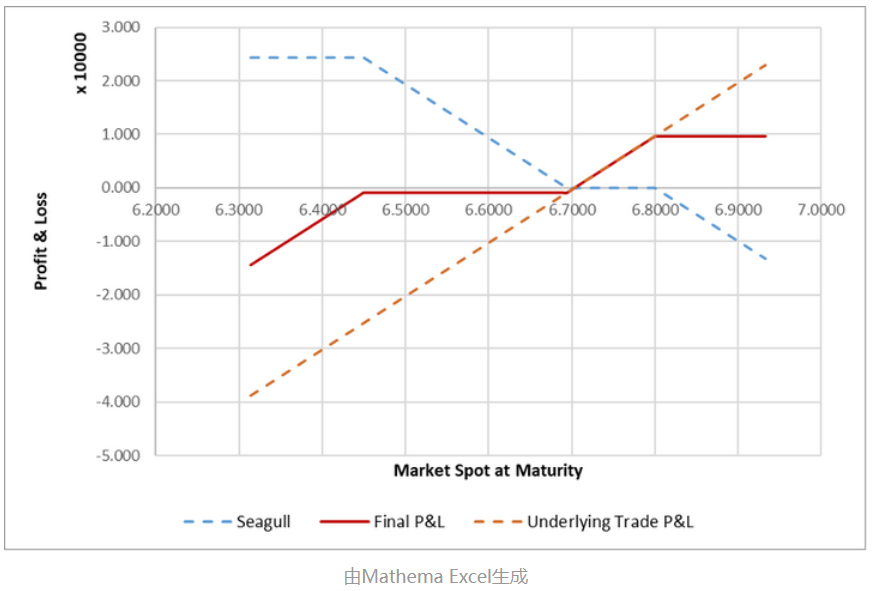
The profit and loss example is shown below:
When combining the impact of the company's export position on exchange rate fluctuations (i.e., the profit and loss after hedging with the Seagull Forward), the result is as follows: