Structured Products for Exchange Rate Hedging – Average Forward
Structured Products for Exchange Rate Hedging – Average Forward
Visit the Mathema Option Pricing System for foreign exchange options and structured product valuation!
Business Overview
The Average Forward consists of a series of forward contracts with a single execution price. Over a period, the client can buy or sell USD/CNY at the agreed execution price on predetermined dates and notional amounts, hence the term "average price." Regardless of the spot exchange rate on the transaction date, the average forward settles at the pre-agreed execution price.
Product Features
Through an average forward, companies can lock in the exchange rate for multiple future transactions in one go, mitigating exchange rate risks. The transaction structure is clear, avoiding the complexity of executing multiple forward contracts with different execution prices. It is suitable for clients who aim to hedge against exchange rate fluctuations, have regular and frequent foreign exchange needs, and wish to manage exchange rate risks through forward transactions.
Pros and Cons Analysis (For Enterprises)
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Mitigates exchange rate risks with a clear transaction structure, locking in the cost of buying or selling foreign exchange. | If the exchange rate continues to rise beyond the execution price, the company cannot benefit from the appreciation. |
Case Study
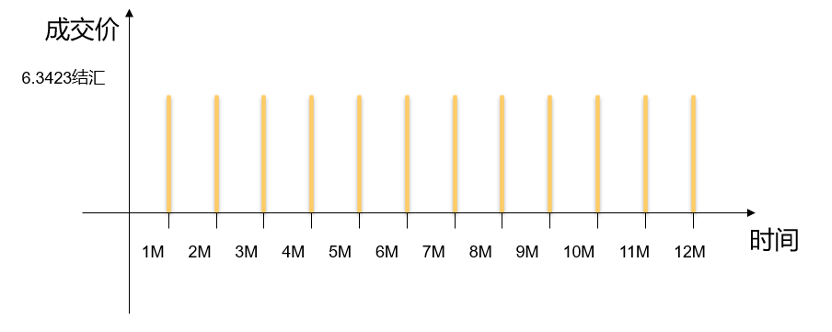
Background: On February 3, 2019, a client expects to receive monthly USD receivables over the next twelve months. The client needs to convert the monthly USD income into CNY for an investment project and wishes to know the conversion cost in advance. They also anticipate that the CNY will appreciate against the USD over the next 12 months.
- Notional Principal: USD 1 million per month.
- Settlement Dates: Monthly settlements over 12 months.
- Execution Price: 6.342300.
- Settlement Description: On the corresponding monthly settlement date, the client sells USD 1 million and buys the equivalent CNY at the execution price.
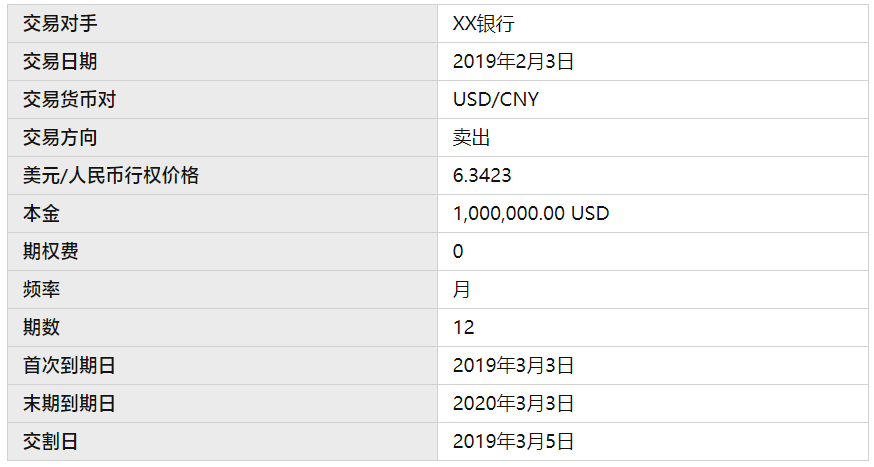
The above scenario can be constructed using a 12-period put option. The transaction details are as follows:
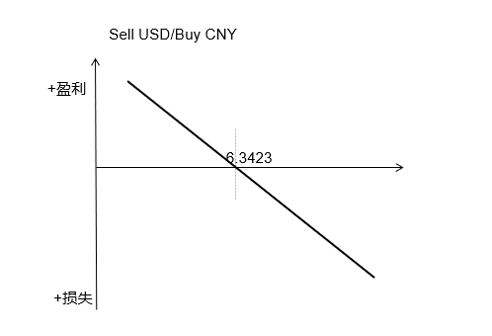
The profit and loss for each period as the exchange rate fluctuates is shown below:
Pricing Analysis
The challenge in pricing an average forward is ensuring that the price for each period is the same and that the overall upfront cost (or option premium) is zero.
We can use an options combination approach for pricing:
- A forward transaction can be decomposed into two options transactions. For a company selling foreign exchange, this can be seen as buying a put option and selling a call option with the same strike price and equal premiums, offsetting each other to zero. This is illustrated below:
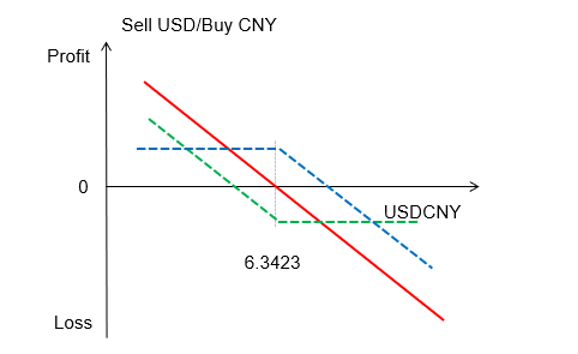
- By using a root-finding method (e.g., the bisection method), we can derive the execution price for the 12-period option with a zero premium. This execution price is the forward price for the average forward.
